Writeup for Hello Ethernaut
- Hello h4ck3r welcome to the world of smart contract hacking. Solving the challenges from Ethernaut will help you understand solidity well.For every challenge they will deploy the contract and give us the instance of that contract and we need to interact with the contract and exploit. Dont worry If you are completely new to solidity and you never deployed smart contract, you can learn deploying the a contract using remix here.
Challenge
- In this level the challenge is to call some functions from the given deployed contract.
Solution
In order to solve this challege you need to interact with some functions in the deployed contract. You need to open developer tools and then you can interact with the functions in the contract using console. You can enter
Ctrl+Shift+Jto open developer toolsOnce you open the developer options, please go through all instructions given by challenge.
If we read the 9th point in instructions they asked us to call
contract.info().info()is a function in the contract deployed for this level. You can typecontract.abiin the console to know all the functions in the deployed contract.Open console and enter the following.
1> await contract.info()
- The function will return ‘You will find what you need in info1().’ So now we need to enter
contract.info1()
1> await contract.info1()
- The above function will return ‘Try
info2(), but with “hello” as a parameter.’
1> await contract.info2("hello")
- The above function will return ‘The property infoNum holds the number of the next info method to call.’
- Here we need to notice that the function
infoNum()will return a value and the returned value can be used to call next info method.
1> await contract.infoNum()
The above function returns a object . You can find a property named words which contains the return value at 0th index and legth of return value at 1st index. The value it returned is 42
If you don’t know what a object is i recommend to learn some basics of OOPS.
Here the function just returned a value but it didn’t asked as to call any function. But if we see the return value of
info2()function it says return value ofinfoNum()can be used to call next info methods.As the return value is 42 the next method we should call is
info42().
1> await contract.info42()
- The above function will return ‘theMethodName is the name of the next method’.
- it says that we need to call a function named
theMethodName().
1> await contract.theMethodName()
- The above function will return ‘The method name is method7123949’.
- It says that we need to call a function named
method7123949().
1> await contract.method7123949()
- The above function will return ‘If you know the password, submit it to authenticate()’.
- From the return value we can conclude that if we call
authenticate()with the correct password this level will be completed. But how can we know the password? Probably there will be a function namedpassword(). - We can know whether the function named
password()exists or not using the contract.abi. ABI refers to Application Binary Interface. It defines the standard way to interact with the function. It contains all the function names existing in the contract with its inputs,outputs etc..
1> contract.abi
- It will return a object containing all the functions in the contract. It is as follows.
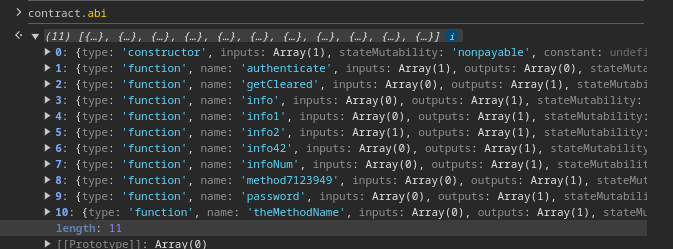
- If we see the abi we can find a function named
password(). Now we need to just call the functionpassword().
1> await contract.password()
- The above function will return ‘ethernaut0’
- Now we need to call
authenticate()with input as ethernaut0 to pass this level.
1> await contract.authenticate("ethernaut0")
- Once you call this function the challenge will be completed. Now you can click on submit instance to complete this challenge.
Key Takeaways
- ABI: ABI refers to Application Binary Interface. It defines how to interact with the smart contract. Understanding abi is necessary to call all the functions.
- To call a function on a contract, you need to provide the required input parameters, which are specified in the ABI. Understanding the input parameters and their data types is essential to successfully calling a function.
***Hope you enjoyed this write-up. Keep on hacking and learning!***
Comments